Reconciliation in orillia & Beyond
Rama Powwow 2022 | Photo by Deb Halbot
Anyone experiencing pain or distress as a result of their residential school experience can access this 24-hour, toll-free and confidential National Indian Residential School Crisis Line at 1-866-925-4419.
Indigenous peoples across Canada can also go to The Hope for Wellness Help Line 24 hours a day, 7 days a week for counselling and crisis intervention. Call the toll-free Help Line at 1-855-242-3310 or connect to the online chat.
local HISTORY


“The Chippewas of Rama First Nation, Chippewas of Georgina Island First Nation, and Beausoleil First Nation were originally part of a larger community known as the Chippewas of Lake Simcoe and Lake Huron of which Chief William Yellowhead (or Musquakie) was recognized as principal chief. As hunter-gatherers, our traditional lifestyle involved following deer herd movements in the autumn and winter months to the West, East, and North points of Ontario. Summer months were spent in settlements at places now known as Atherley, Orillia and Coldwater.
In the 1830’s, on behalf of the Crown, Lieutenant-Governor Sir John Colborne set aside a clearing of approximately 10,000 acres for our nation between the Narrows (where Lake Couchiching and Lake Simcoe meet) and Coldwater. The government tried to gather our people together to make them farmers. This was also the beginning of the reserve system which continues today.
During their settlement in the area, our ancestors were successful in establishing the foundations for their communities, building the Coldwater Grist Mill, which still stands in the town of Coldwater, and clearing the way for the route now known as Ontario Highway No. 12. In 1836, the Chiefs signed a document that they understood would provide title to the land but was actually a surrender which gave up the reserve lands.
At that point, what was a large nation of 3 communities, was separated. Chief Aisance and his band moved to Christian Island; Chief Snake and his band eventually located in Georgina Island; and Chief Yellowhead and his band stayed in this area and are now known as the Chippewas of Rama First Nation. These three First Nations, together known as the Chippewa Tri-Council, still enjoy a strong relationship today. In 2012, the Chippewa Tri-Council settled a claim with the federal government for the Coldwater Narrows Land. It was largest specific claims settlement in Canadian history at that time.”
Information sourced from Rama First Nation
What treaty territory is Orillia on?
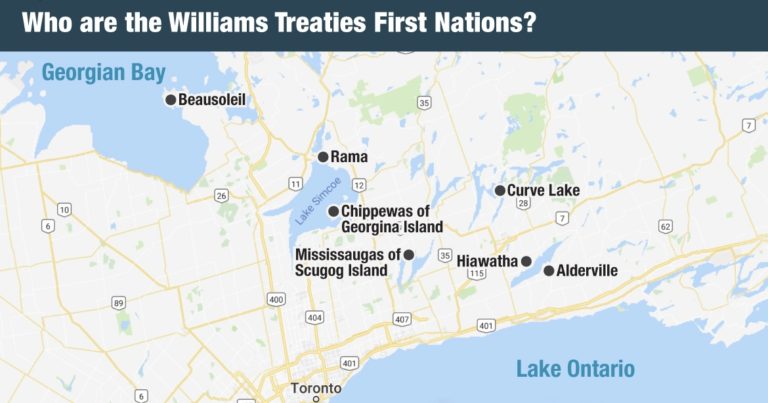
Orillia falls within the Williams Treaties territory.
The Williams Treaties were signed on October 31 and November 15, 1923, by seven Anishinaabe First Nations and representatives of the Crown. A commission was established by Canada and led by Treaty Commissioner A.S. Williams to address lands that had not been surrendered via treaty.
The territory covered by the Williams Treaties stretched from the northern shore of Lake Ontario to Lake Nipissing, and together cover approximately 52,000 km². The geography of the Treaties overlaps with several previous treaties.
The seven Williams Treaties First Nations are: Alderville First Nation, Chippewas of Beausoleil First Nation, Chippewas of Georgina Island First Nation, Chippewas of Rama First Nation, Curve Lake First Nation, Hiawatha First Nation and Mississaugas of Scugog Island First Nation.
Source: https://www.ontario.ca/page/map-ontario-treaties-and-reserves#treaties
In 2018, the Williams Treaty First Nations reached a settlement agreement with the government.
The claim:
- Crown did not act honourably when making and implementing Williams Treaties:
- proper compensation and additional lands not provided in 1923
- First Nations’ harvesting rights unjustly denied
The negotiated Settlement Agreement:
- Recognition of pre-existing treaty harvesting rights for First Nations members in certain treaty areas
- Federal and provincial apologies for negative impacts of the Williams Treaties on First Nations
- Financial compensation: $666 million from Canada and $444 million from Ontario
- Additional reserve lands: each First Nation can acquire and apply to add up to 11,000 acres to their reserve land base
Videos by Kory Snache from Rama First Nation
This visual documentary explores the Indigenous and Anishnaabeg history of the rivers of Mskwaaki, also known as Muskoka. It focuses on the use of five rivers in what is now commonly known as Muskoka by the Ojibweg of Rama.
The story of how Nanabush shaped Gojienjawjeen. The lake more commonly known as Couchiching. Told by Fred King(ban) to Norm Stinson from Rama Ojibwe Reserve.
***IMPORTANT LOCAL FUNDRAISER***:
"Help me preserve the Eastern Ojibwe language"
COMMUNITY RESOURCES IN THE ORILLIA AREA
Mamaway Wiidokdaadwin Primary Care Team

Georgian Bay Native Friendship Centre

Georgian Bay Native Women's Association

Barrie Native Friendship Centre

Rama First Nation Culture and Heritage

Biminaawzogin Regional Aboriginal Women's Circle
Georgian Bay Metis Council
NSM Healthline - Services for Indigenous Peoples

Dnaagdawenmag Binnoojiiyag Child & Family Services (DBCFS)

Enaahtig Healing Lodge & Learning Centre

Métis Nation of Ontario

Orillia Native Women’s Group (ONWG)

GEORGIAN COLLEGE

LAKEHEAD UNIVERSITY

Truth and Reconciliation in Canada
The Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada was a truth and reconciliation commission active in Canada from 2008 to 2015, organized by the parties of the Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement.
The commission was officially established on June 1, 2008, with the purpose of documenting the history and lasting impacts of the Canadian Indian residential school system on Indigenous students and their families. It provided residential school survivors an opportunity to share their experiences during public and private meetings held across the country. The TRC emphasizes that it has a priority of displaying the impacts of the residential schools to the Canadians who have been kept in the dark from these matters.
In June 2015, the TRC released an executive summary of its findings along with 94 “calls to action” regarding reconciliation between Canadians and Indigenous Peoples. The commission officially concluded in December 2015 with the publication of a multi-volume final report that concluded the school system amounted to cultural genocide. The National Centre for Truth and Reconciliation, which opened at the University of Manitoba in November 2015, is an archival repository home to the research, documents, and testimony collected during the course of the TRC’s operation.
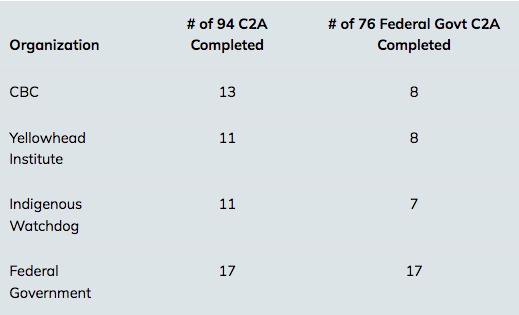
It is important to note that almost 8 years after the 94 Calls to Action were released, not nearly enough progress has been made by the Federal Government.
The federal government states that they have completed 17 Calls to Action as per the following table vs CBC (8), Yellowhead Institute (8) and Indigenous Watchdog (7) ranking of those same 17 Calls to Action: